News Archive
Berkeley Lab Receives $4 Million in Recovery Act Funding to Develop Computational Methods for Energy-Related Research
Researchers in the Computational Research Division (CRD) of the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE's) Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have received more than $4 million in funding for six projects that will help develop computational methods to answer some of the nation's most pressing questions regarding energy efficiency, climate stabilization, and next-generation, carbon-neutral energy sources. Read More »
Science at Scale: SciDAC Astrophysics Code Scales to Over 200K Processors
Performing high-resolution, high-fidelity, three-dimensional simulations of Type Ia supernovae, the largest thermonuclear explosions in the universe, requires not only algorithms that accurately represent the correct physics, but also codes that effectively harness the resources of the next generation of the most powerful supercomputers. Read More »
Berkeley Lab Team Receives NASA Public Service Group Achievement Award
Three scientists from the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory’s (Berkeley Lab) Computational Cosmology Center (C3) are being honored with a NASA Public Service Group Award for developing the supercomputing infrastructure for the U.S. Planck Team’s data and analysis operations at the Department of Energy's National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC). Read More »
How a Summer Internship—or a Weekend Lecture—Can Change a Life
Emily Chen still vividly remembers the lecture on gecko feet. She was an eighth grader attending Berkeley Lab’s Nano*High program to hear materials scientist Arun Majumdar explain how what he was learning about gecko feet might translate into a new adhesive product based on carbon nanotubes. Read More »
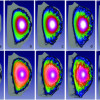
Computers Give Insights into Generating Power Like the Sun
If humans could harness nuclear fusion, the process that powers stars like our Sun, the world could have an inexhaustible energy source. In theory, scientists could produce a steady stream of fusion energy on Earth by heating up two types of hydrogen atoms—deuterium and tritium—to more than 100 million degrees centigrade until they become a gaseous stew of electrically charged particles, called plasma. Then use powerful magnets to compress these particles until they fuse together, releasing energy in the process. Read More »
Data Acquisition and Coordination Key to Human Microbiome Project
At birth, your body was 100-percent human in terms of cells. At death, about 10 percent of the cells in your body will be human and the remaining 90 percent will be microorganisms. That makes you a “supraorganism,” and it is the interactions between your human and microbial cells that go a long way towards determining your health and physical well-being, especially your resistance to infectious diseases. Read More »
Grace Hopper Powers Science on NERSC's New Cray XE6
American computer scientist Grace Hopper will power science on the cabinets of the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center's (NERSC) petascale Cray XE6 system. A pioneer in the field of software development and programming languages, Hopper created the first compiler. She was a champion for increasing the usability of computers, understanding that their power and reach would be limited unless they were made to be more user-friendly. NERSC's new flagship machine is named "Hopper" in her honor. Read More »
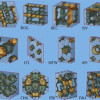
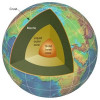
Simulations Reveal That Earth's Silica Is Predominantly Superficial
Silica is one of the most common minerals on Earth. Not only does it make up two-thirds of our planet's crust, it is also used to create a variety of materials from glass to ceramics, computer chips and fiber optic cables. Yet new quantum mechanics results generated by a team of physicists from Ohio State University (OSU) show that this mineral only populates our planet superficially—in other words, silica is relatively uncommon deep within the Earth. Read More »
Berkeley Lab Scientists Build Software Framework for ATLAS Collaboration
Three thousand researchers in 37 countries are searching for the origins of mass, new dimensions of space and undiscovered forces of physics in the head-on collisions of high-energy protons at the Large Hadron Collider's ATLAS experiment. When ATLAS is turned-on, its detectors record about 400 collision events per second from a variety of perspectives, a rate equivalent to filling 27 compact disks per minute. Read More »
Victor Markowitz Appointed JGI CIO and Associate Director
The Director of the Joint Genome Institute (JGI), Eddy Rubin, has announced that Victor Markowitz will serve as the new Chief Informatics Officer and Associate Director at JGI effective May 17, 2010. Read More »







 Instagram
Instagram YouTube
YouTube