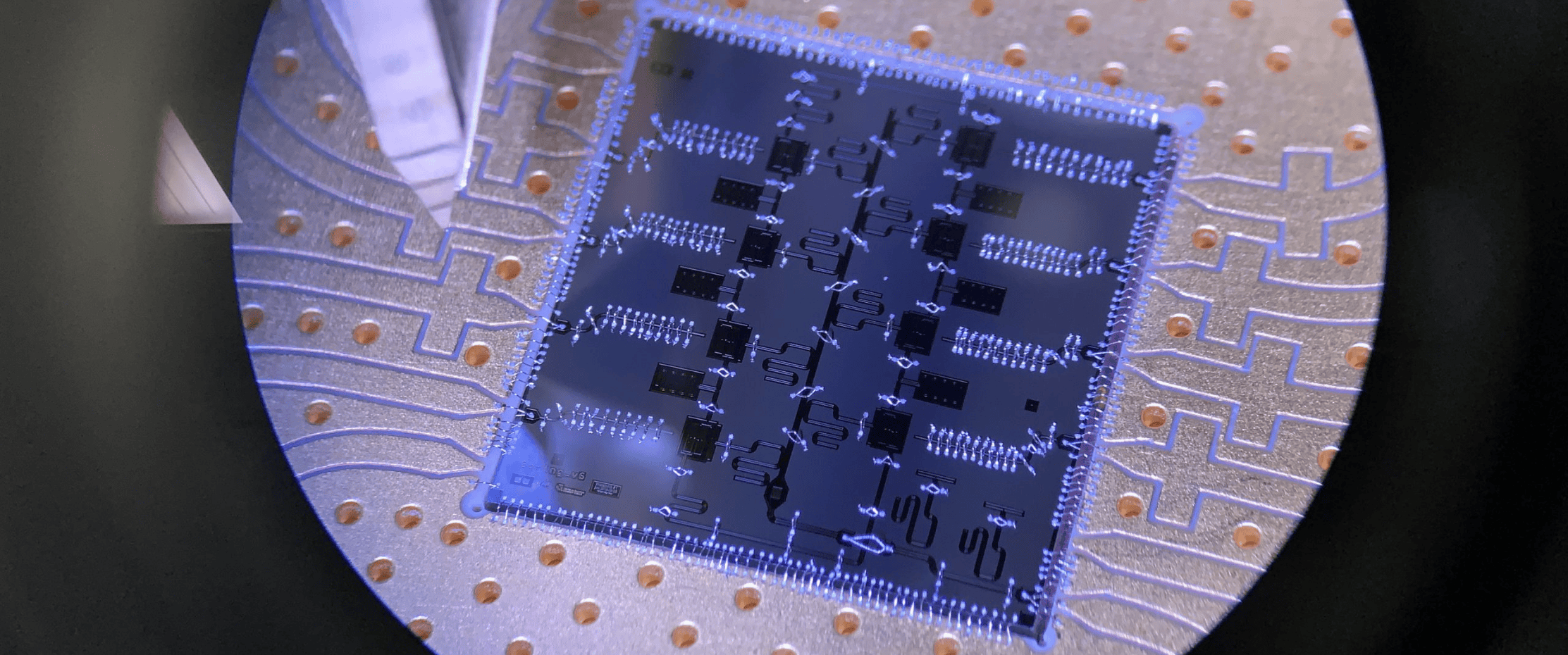
Berkeley Lab’s Computing Sciences Area is at the forefront of harnessing quantum information science and technology to drive discoveries that will improve our lives—from developing new materials to ensuring secure communications.
We are pioneering advancements across the quantum research ecosystem, from theory to application, by partnering with industry and academia. Together, we fabricate and test quantum-based devices, develop software and algorithms, build prototype computers and networks, and apply these innovations to achieve breakthroughs in physics and chemistry.
Quantum Systems Accelerator (QSA)

The QSA, one of the Department of Energy’s National Quantum Information Science Research Centers, brings together national labs, industry, and universities to tackle critical challenges in quantum information science, foster research collaboration, and train the next generation of quantum scientists and engineers.
Advanced Quantum Testbed (AQT)
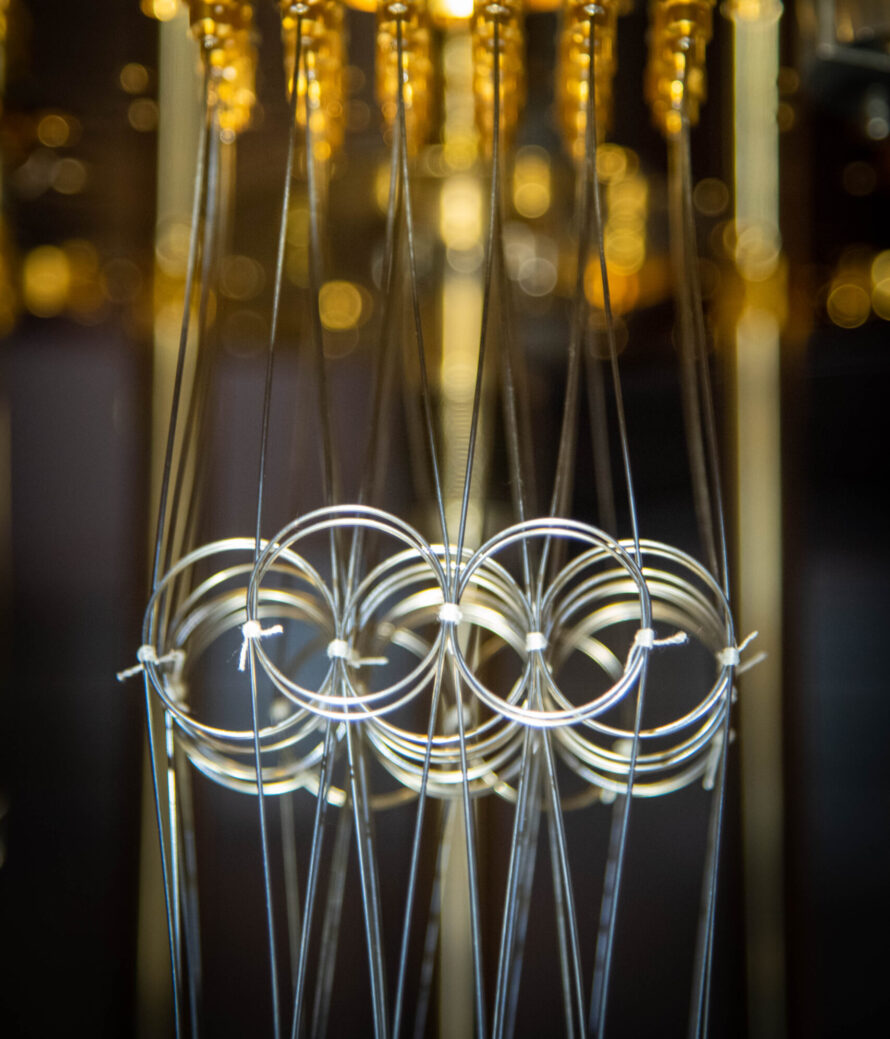

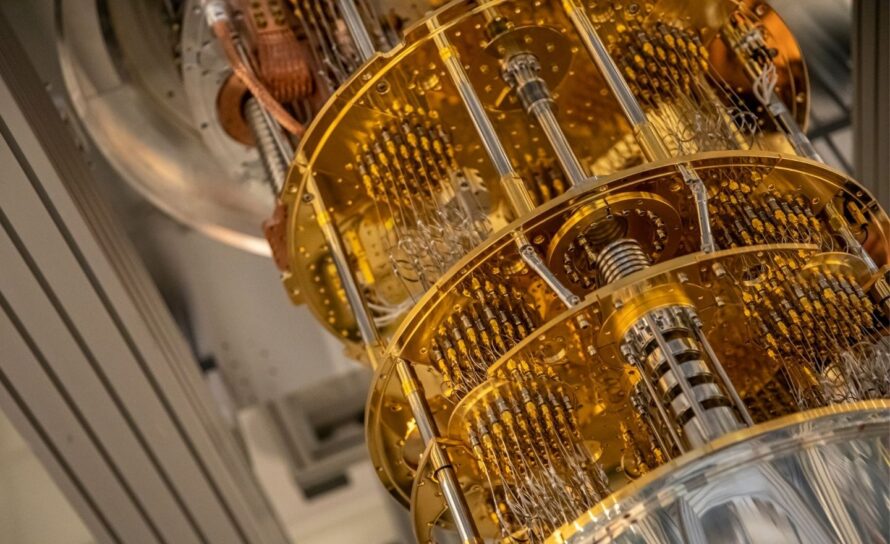
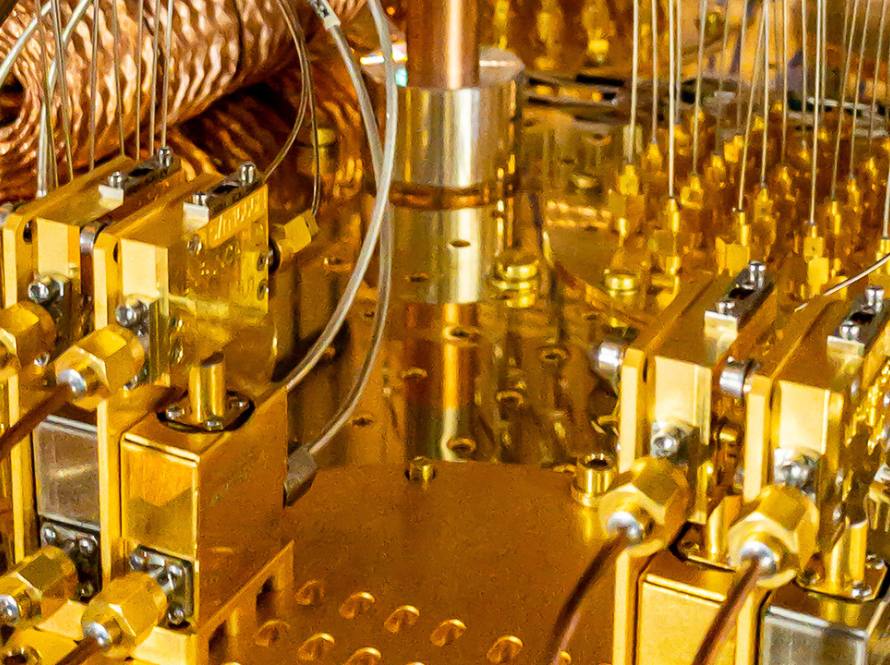
AQT is a collaborative laboratory that designs, fabricates, and operates superconducting quantum processors. It enables scientists to co-develop and implement quantum algorithms for solving challenging problems in optimization, materials science, and high-energy physics, utilizing open-access, intermediate-scale quantum hardware.
QUANT-NET

QUANT-NET leverages world-leading expertise in quantum technologies, optics, materials, networks, testbed operations, and other assets from Berkeley Lab, UC Berkeley, and Caltech. It aims to build a software-controlled, application-focused quantum computing network between Berkeley Lab and UC Berkeley based on entanglement.
QIS at NERSC

QIS at NERSC is a program that provides compute time on Perlmutter for projects advancing quantum information science, including quantum algorithm development, simulation, and integration with high-performance computing. The initiative supports research collaborations between academia, industry, and Berkeley Lab to accelerate breakthroughs in quantum technologies.
MACH-Q

Modular and Error-Aware Software Stack for Heterogeneous Quantum Computing Ecosystems (MACH-Q) is developing a modular, readily expandable, and error-aware quantum software stack. These capabilities will enable plug-and-play deployment in emerging heterogeneous and distributed quantum computing environments, as well as integration with third-party software.
Berkeley Quantum Synthesis Toolkit (BQSKit)
BQSKit is a superoptimizing quantum compiler and research platform that integrates ideas from multiple Berkeley Lab projects into an accessible and easily extensible software suite.
Superconducting Race Logic Accelerators

Superconducting race logic accelerators are ultra-fast, energy-efficient computing devices that use superconducting electronics to advance classical computation, leveraging technologies and fabrication methods also foundational to quantum computing research.
HamPerf

HamPerf is a quantum benchmarking approach that evaluates the computational utility of quantum processors by focusing on the underlying mathematical descriptions (Hamiltonians) of problems, enabling fair comparisons across different hardware and algorithms.
Cryogenic Control for Quantum

Cryogenic Control for Quantum explores innovative low-temperature control solutions using superconducting technology to enable scalable, high-fidelity control of quantum systems, overcoming the limitations of current room-temperature and cryo-CMOS approaches.
FABLE

FABLE is a software tool that efficiently generates quantum circuits to represent large, dense matrices—enabling advanced quantum algorithms by embedding these matrices into quantum operations with minimal computational overhead.
AQuA-DATA
AQuA-DATA (Advanced Quantum Algorithms for Diverse Applications and Theoretical Advancements in Science), is aimed at creating new quantum algorithms with applications across various scientific fields. This work will contribute to optimizing quantum computation for diverse real-world problems, making quantum technology more accessible for practical use.
QCaMP
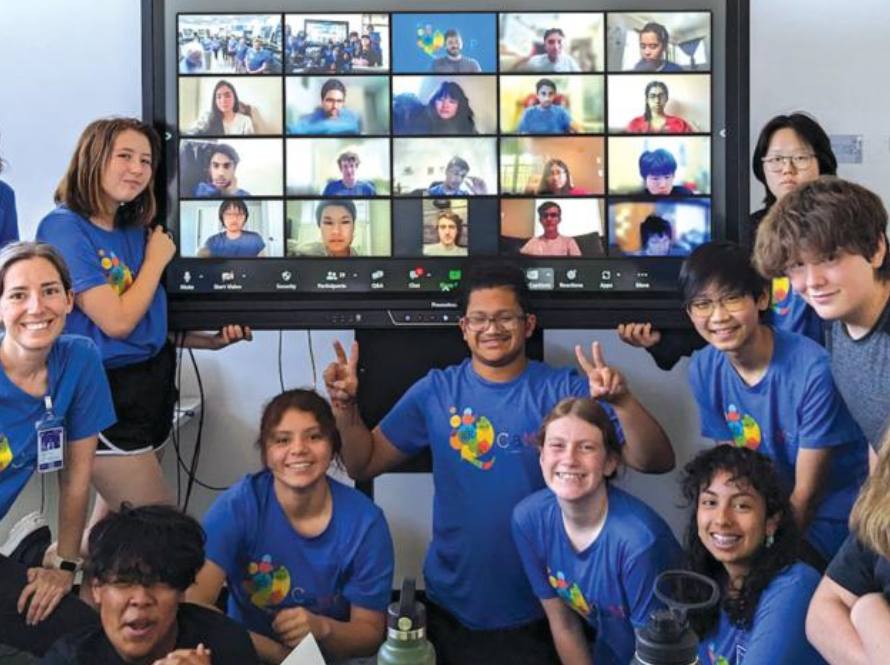

QCaMP (Quantum, Computing, Mathematics, & Physics) is a free, hands-on summer camp hosted by Berkeley Lab that introduces high school students and teachers to the fundamentals of computing and quantum physics, offering practical experience with quantum circuits and real-world quantum computers, with programs available in the Bay Area and partner locations nationwide.
Quantum Chip Hero Run

Seven Ways Berkeley Lab is Pioneering the Quantum Future

Science Power-Up: Rewriting the Rules with Quantum