A Data Science Pioneer, Deb Agarwal Retires From Berkeley Lab
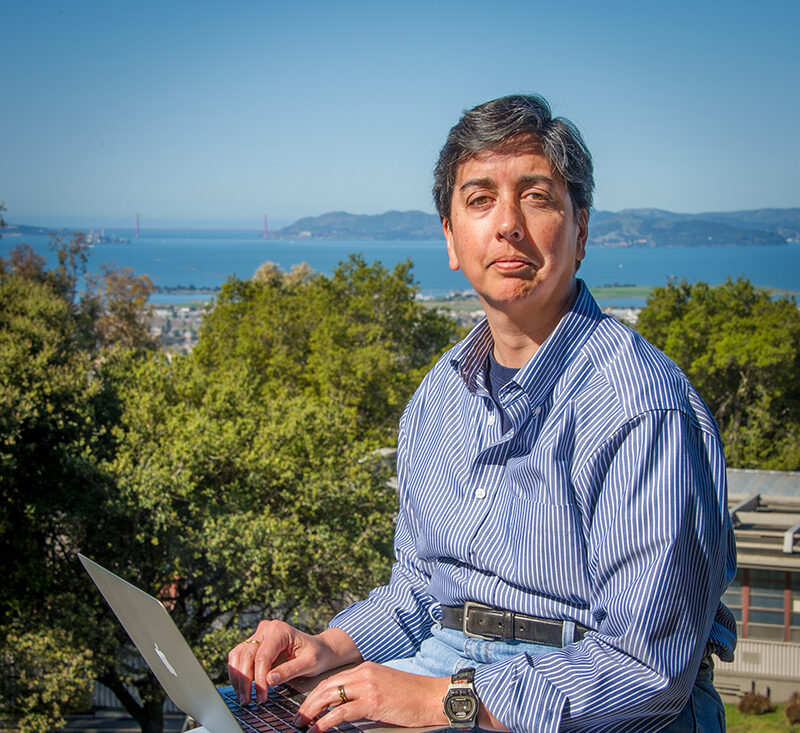

Katie Antypas to Oversee Advanced Cyberinfrastructure at NSF
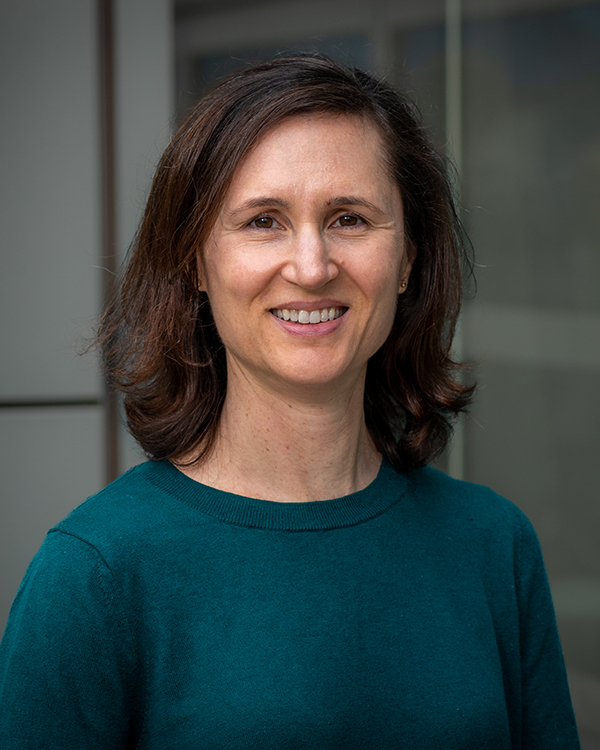

Rollin Thomas Recognized for Contributions to Project Jupyter

Richard Gerber Named Hardware and Integration Director for ECP

ExaLearn Expands Horizons with Surrogate Modeling
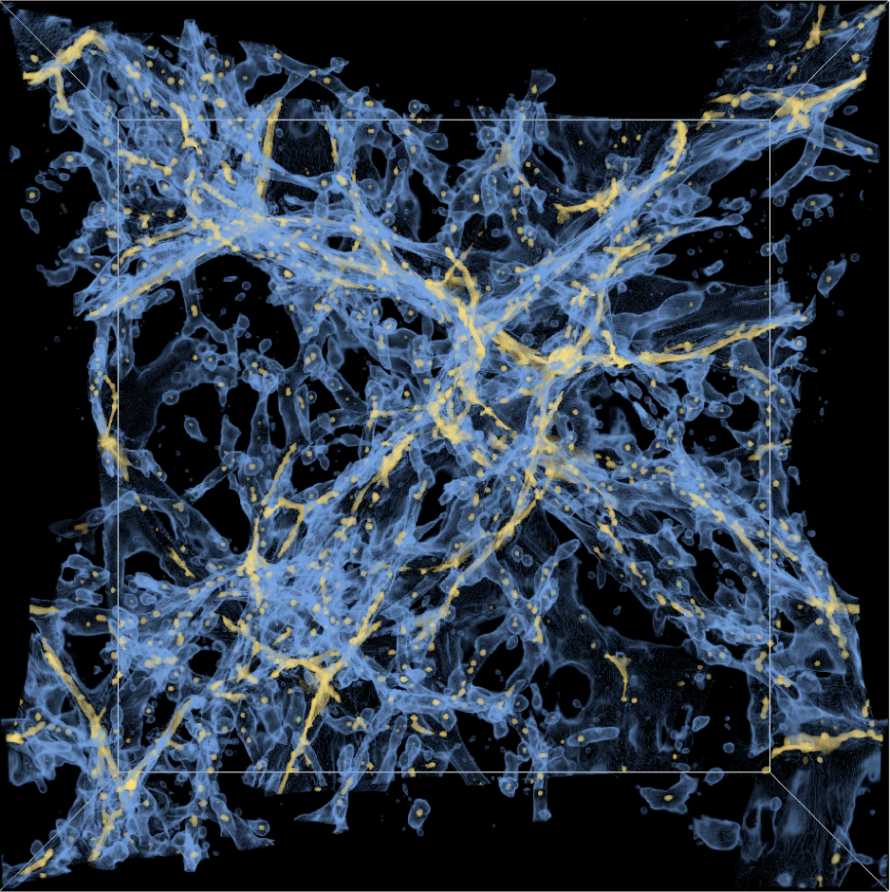
Berkeley Lab Plays Major Role in Developing the DOE Vision for AI

Berkeley Lab Celebrates 20 Years of the Alvarez Fellowship

NERSC Supports First All-GPU Full-Scale Physics Simulation
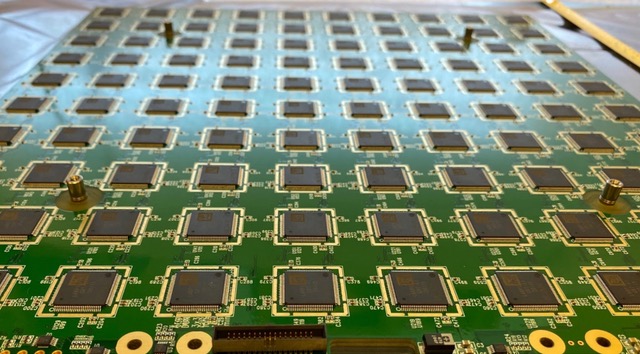
Berkeley Lab Computing Sciences Takes Novel Approach to Science Workforce Development and Diversity
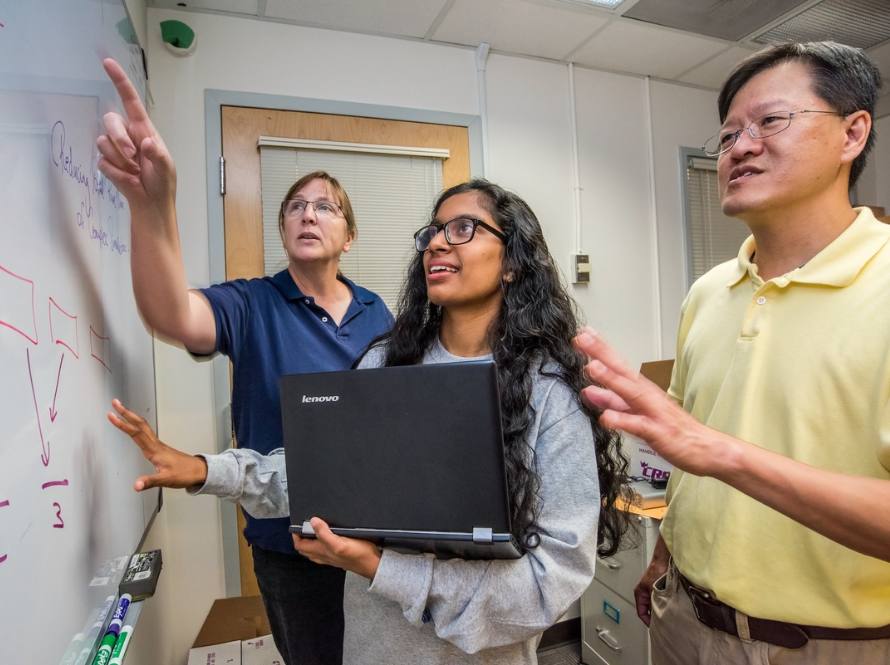

CSA Summer Program Welcomes a Record 180 Participants

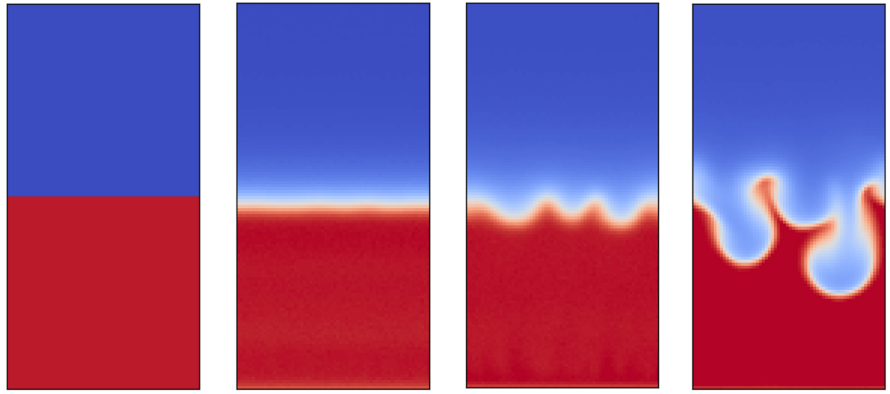
Berkeley Lab’s Novel Method for Modeling Fluids at the Mesoscale
NERSC and the HPC Community Bid Farewell to Cori Supercomputer


