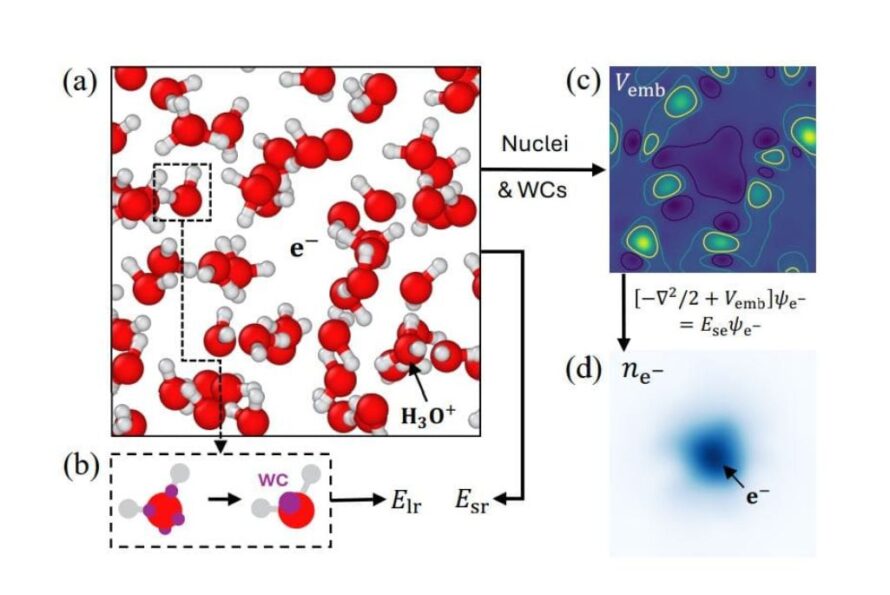
New AI-Powered Hybrid Simulation Reveals How Electrons Drive Chemical Reactions in Liquids
Unlocking the Power of Quantum Computing with Practical Benchmarking Tools
Software Highlight: Fiats Brings Deep Learning to Fortran at Supercomputer Scale

Software Highlight: Julienne and Assert Strengthen Fortran Code Reliability

Software Highlight: Caffeine Supercharges Fortran for the Exascale Era

Berkeley Researchers Receive IEEE Best Paper Award for Exascale Software Insights

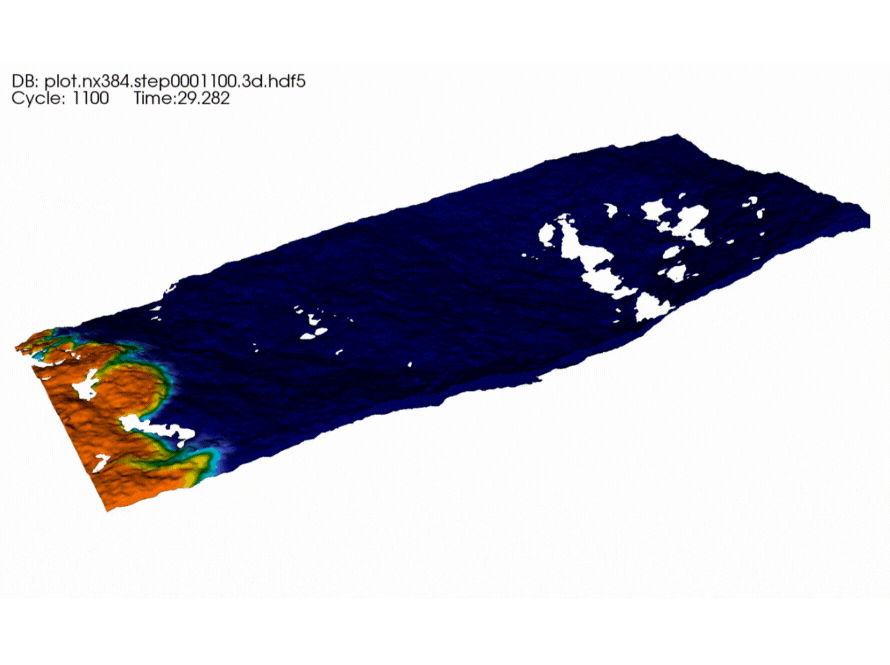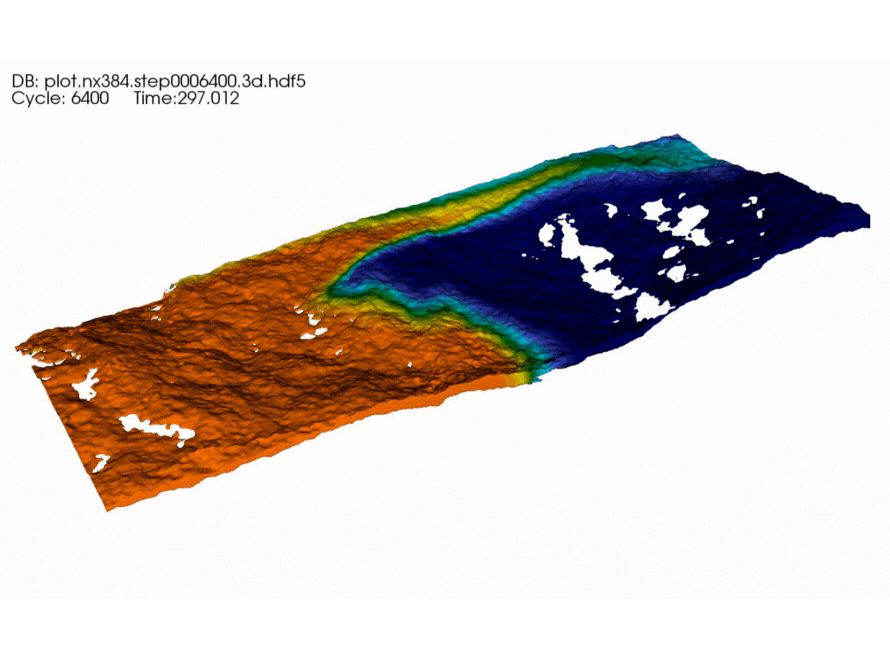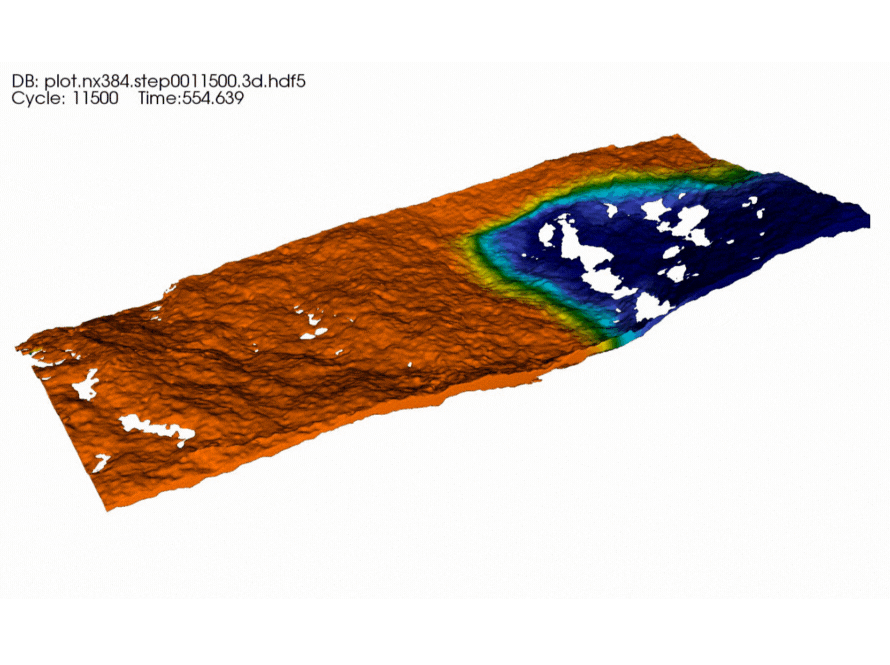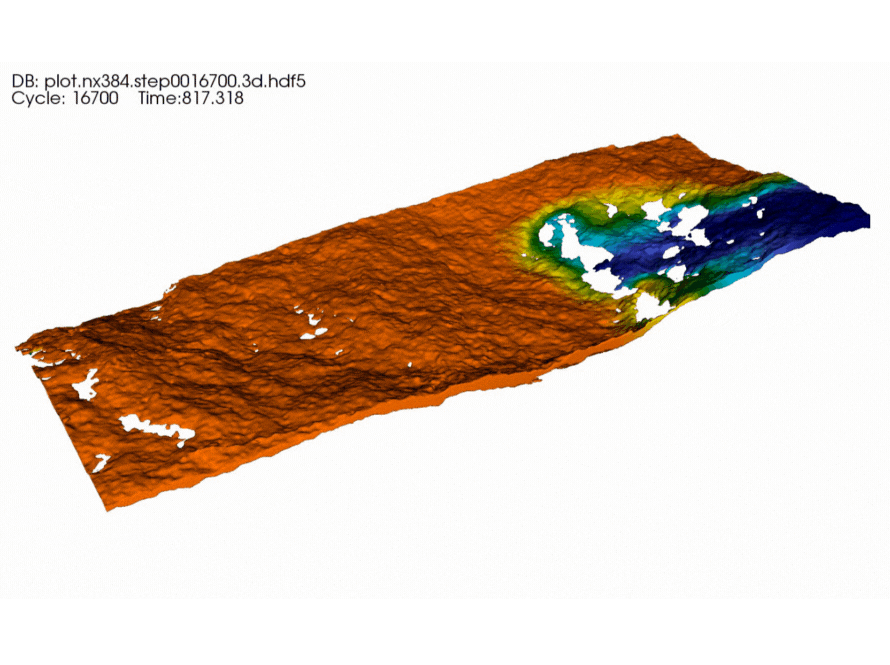
Berkeley Researchers Advance Fluid Flow Modeling for Better Energy Production
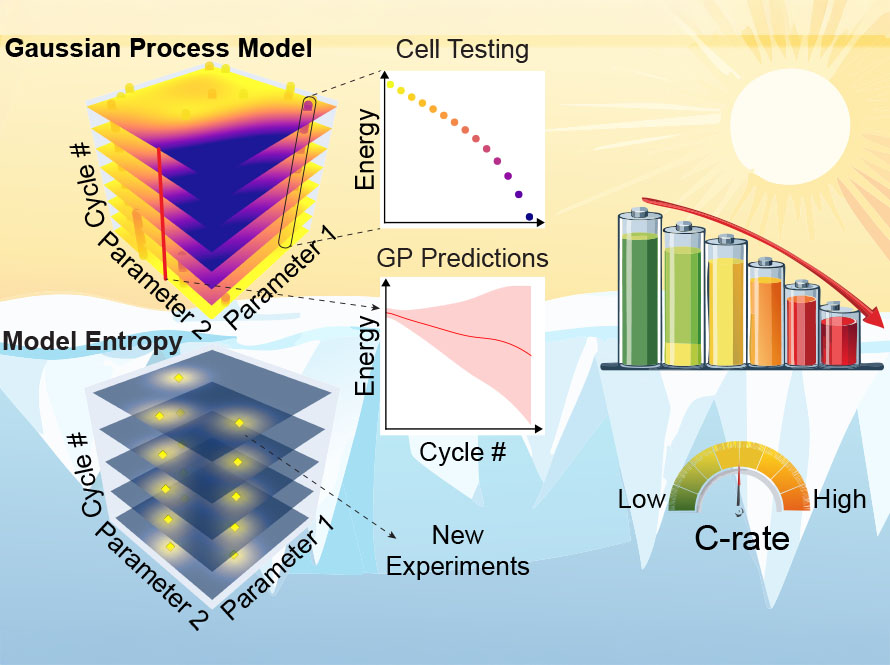
Machine Learning Breakthrough Transforms Battery Lifespan Prediction
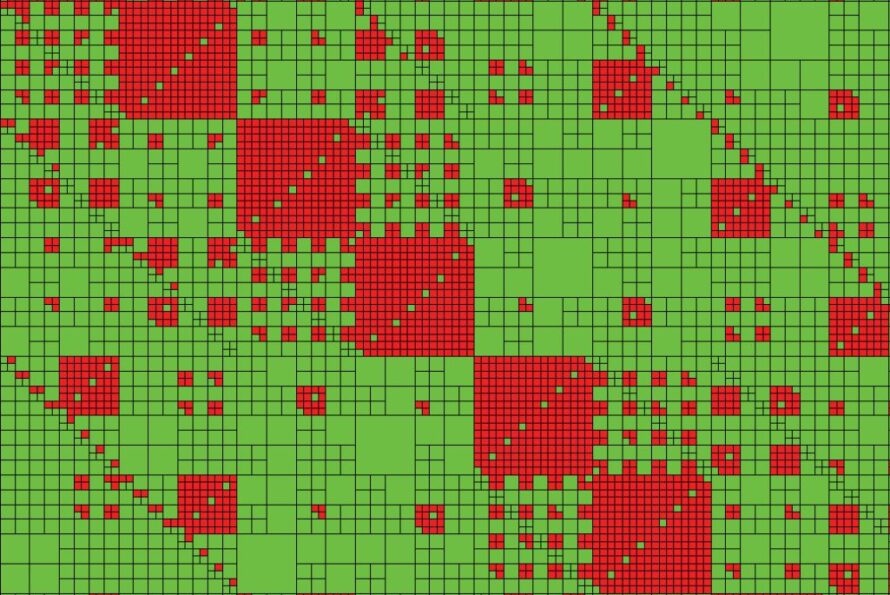
Science Highlight: Breakthrough Computing Method Speeds Up Big Calculations for Science and Engineering
Meet Mark Fornace, Berkeley Lab’s 2025 Alvarez Fellow

Computational Chemistry Unlocked: A Record-Breaking Dataset to Train AI Models has Launched

Berkeley Lab Researchers Awarded ARITH 2025 Best Paper


