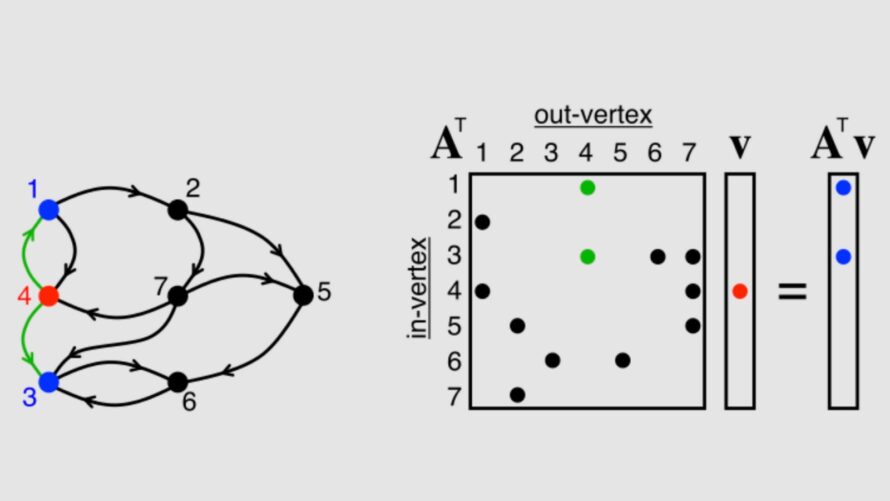
Science Highlight: Specialized Hardware Helps Researchers Quickly Process Sparse Matrices
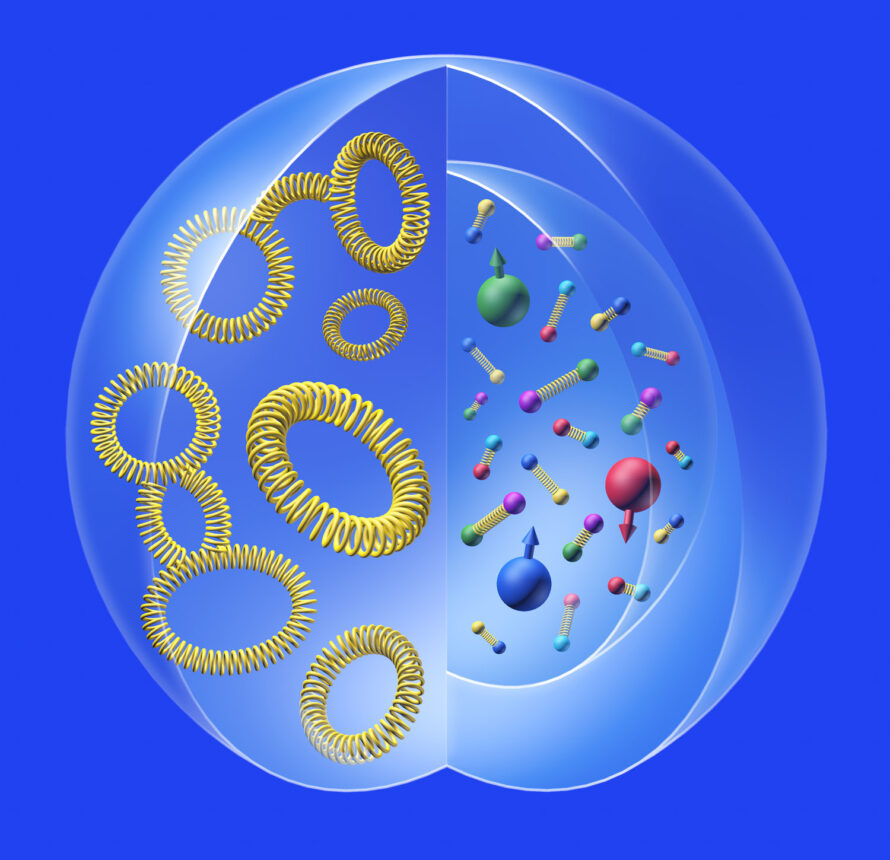
Gravitational Form Factors Illuminate Substructure of the Proton
Zaida McCunney Retires After 25 Years at Berkeley Lab

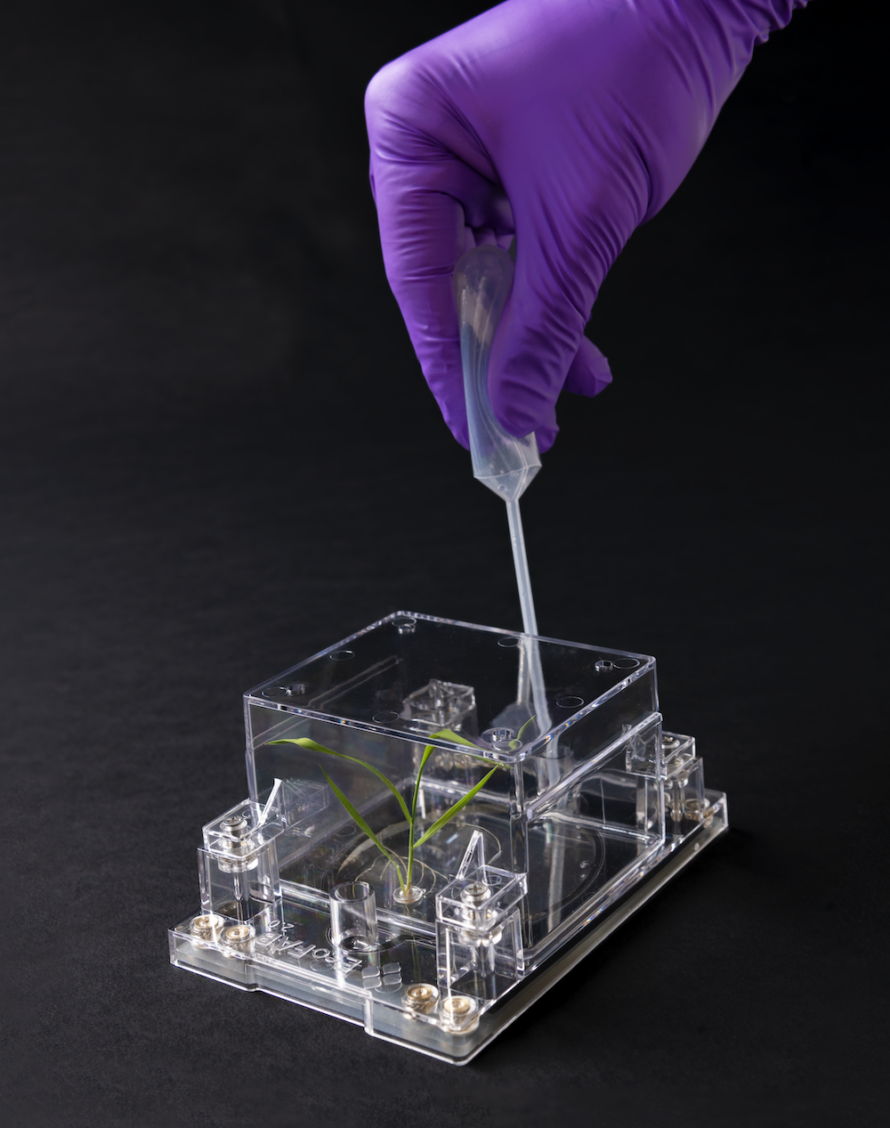
Berkeley Lab Researchers Advance AI-Driven Plant Root Analysis

SciData Director Kupresanin Honored as ASA Fellow

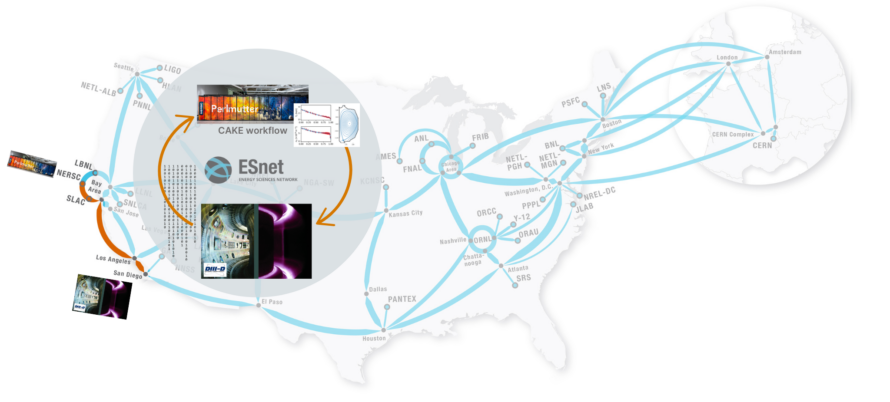
DIII-D National Fusion Facility, NERSC, AMCR, and ESnet Collaboration Speeds Nuclear Fusion Research
The Power of Numerical Analysis in Quantum Chemistry

Unraveling Brain Complexity
Celebration Spotlights Phil Colella’s Remarkable DOE Career

Berkeley Lab Dives into HPC’s Future at ISC 2024

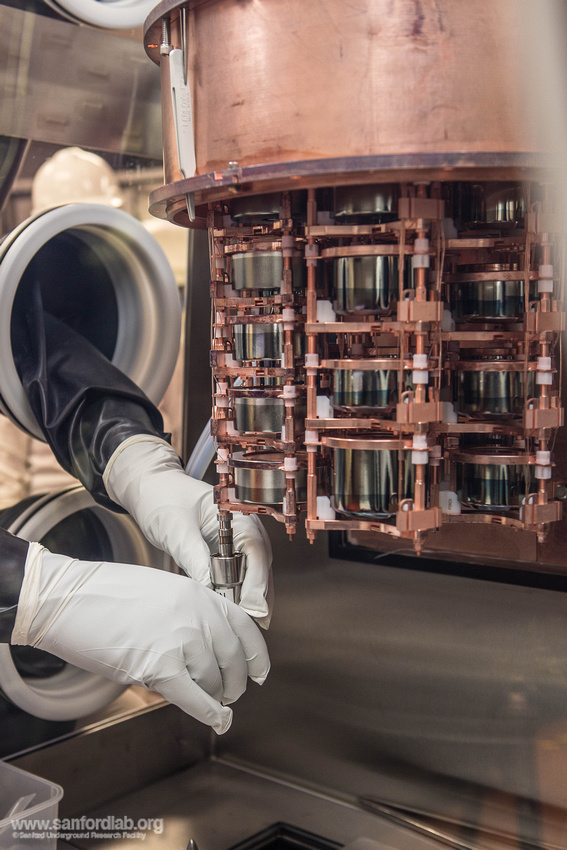
NERSC Aids Hunt for "Cracks" in the Standard Model

Quantum Insights: Innovating Data Representation, Analysis, and Visualization


