News
Floating Robots Track Water Flow, Stream Data via Smartphones
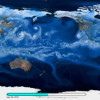
Two-thirds of the water in California passes through the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta, providing drinking water for 22 million Californians and supporting agriculture valued at tens of billions of dollars. Read More »
After 5 Years, NERSC’s Franklin Retires
This week, the Department of Energy’s National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC) retired one of its most scientifically prolific supercomputers to date—a Cray XT4 named Franklin, in honor of the United States’ pioneering scientist Benjamin Franklin. Read More »
John Bell Elected to National Academy of Sciences
BERKELEY, Calif. – John Bell, an applied mathematician and computational scientist who leads the Center for Computational Sciences and Engineering and the Mathematics and Computational Science Department at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, has been elected to the National Academy of Sciences. Read More »
A 100-Gigabit Highway for Science
In an effort to spur U.S. scientific competitiveness, as well as accelerate development and widespread deployment of 100-gigabit technology, the Advanced Networking Initiative (ANI) was created with $62 million in funding from the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA) and implemented by ESnet. ANI was established to build a 100 Gbps national prototype network and a wide-area network testbed. Read More »
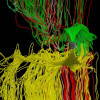
Visualizing Processes That Lead to “Cracks” in the Earth’s Cocoon
The Sun makes all life on Earth possible. Among its many life-sustaining functions, this star regulates our climate and provides an unlimited source of energy. The Earth is also electromagnetically connected to the Sun, and this relationship exposes our planet to violent solar storms. Unlike Earth, Sun’s atmosphere is not contained but blows across our solar system, a phenomenon called solar wind, which consists of charged particles and an embedded magnetic field. Read More »
Albany, Berkeley High School Girls Present Apps Developed in Lab-Supported Program
Eleven teams of high school girls who have been meeting with mentors at Berkeley Lab since February to develop science education apps for smartphones gave their best pitches for their work Saturday, with a team from Albany High taking top honors for StudiCafe, an app aimed at helping students study for college-level Advanced Placement courses with social networking added to maintain interest. Read More »
Eli Dart Tackles ESnet's Science DMZ
The U.S. Department of Energy’s Energy Sciences Network, or ESnet, provides reliable high-bandwidth network services to thousands of researchers tackling some of the most pressing scientific and engineering problems, such as finding new sources of clean energy, increasing energy efficiency, understanding climate change, developing new materials for industry and discovering the nature of our universe. To support these research endeavors, ESnet connects scientists at more than 40 DOE sites with… Read More »
Berkeley Lab Hosts Albany High Students on Job Shadow Day
For the fourth year in a row, Berkeley Lab staff hosted juniors from Albany High School as part of the school's annual Job Shadow Day. The event matches students with mentors in areas of interest specified by the students. Read More »
New to Computing Sciences - March 2012
Pardeep Pall, Visualization and Analytics Group and James Lee, Computing Sciences IT Infrastructure Team Lead Read More »
New Computer Codes Unlock the Secrets of Cleaner Burning Coal
Approximately half of all electricity used in the United States comes from coal. When burned, this fossil fuel emits pollutants that contribute to smog, acid rain and increased greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. But as the demand for power increases, and affordable renewable energy sources remain years away from offsetting this need, one fact is clear: Coal is here to stay, at least for the foreseeable future. Read More »







 Instagram
Instagram YouTube
YouTube